Optimize Your Environmental, Social, Governance (ESG) By Automating the Process
Authors: Saj Abraham (Director of Stratroom), Dr. Naresh Makhijani (CEO of OTI), Sherni Makhijani (Social Media Specialist)

ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) reporting has become critical for measuring an organization’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices. It goes beyond just financial performance and delves into how ann organization manages risks and opportunities related to the environment, its social impact, and its internal governance structure. By considering these factors, ESG seeks to provide a more holistic picture of an organization’s long-term viability and its contribution to a just and sustainable future.
There is a continued rise in ESG adoption among global investors, with 89% incorporating ESG factors in their investment decisions in 2022. Europe leads the charge with the highest number of ESG users, while North America and Asia-Pacific follow behind.
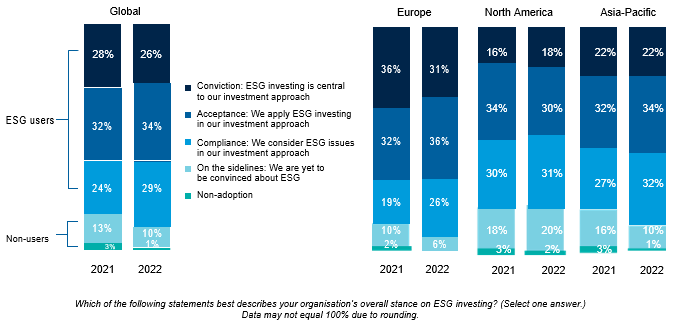
Investors are making adjustments and improvements to their ESG investment approaches. There’s a surge in organizations reporting on ESG factors. Over 90% of S&P 500 organizations and roughly 70% of Russell 1000 organizations now publish ESG reports in some format (Mckinsey, 2022).
Challenges in Manual ESG Reporting
While implementing a strong ESG strategy is critical, manual processes create significant roadblocks. A Capital Group study (2022) identified key challenges: inconsistent ESG ratings, difficulty accessing data, and limited performance measurement capabilities. These challenges can come from a number of obstacles. 53% practitioners worldwide also said the biggest obstacle to adopting sustainable investing was the poor quality or limited availability of ESG data and analytics (BlackRock, 2020).
One major hurdle lies in data collection and aggregation. ESG data often resides in siloed departments and systems across a organization, making it difficult to gather and ensure its accuracy and consistency. This fragmented approach can lead to incomplete reports and undermine a organization’s ability to track progress over time.
Navigating the complexities of ESG reporting standards is time-draining. Integrating these principles seamlessly into daily operations requires a strategic shift, and organizations grappling with short-term pressures may find it difficult to justify long-term sustainability investments. The manual effort required for compiling reports diverts resources from core business activities. Resource constraints, from financial limitations to expertise gaps, also gets in the way of progress.
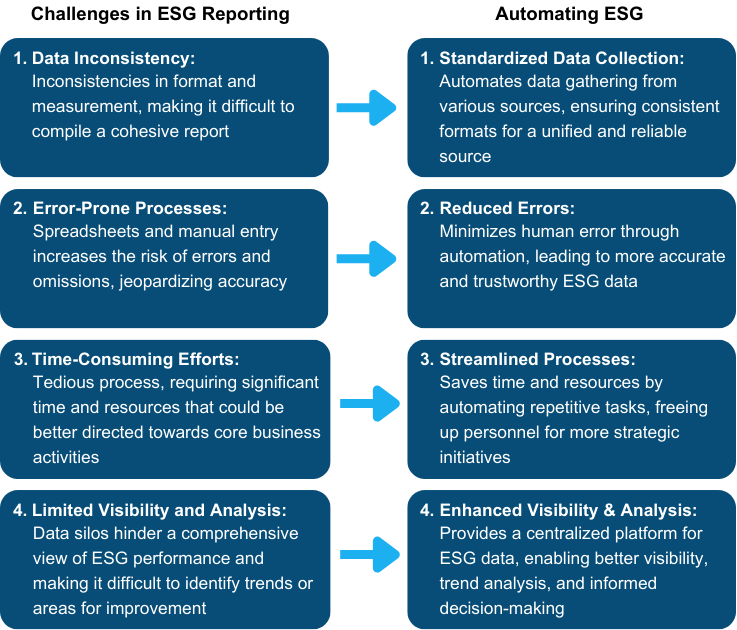
Challenges in ESG Reporting
Data Inconsistency: Manually gathering ESG data from various sources leads to inconsistencies in format and measurement, making it difficult to compile a cohesive report.
Error-Prone Processes: Reliance on spreadsheets and manual entry increases the risk of errors and omissions, potentially jeopardizing the accuracy of the organization’s ESG report.
Time-Consuming Efforts: Manual ESG reporting is a tedious process, requiring significant time and resources that could be better directed towards core business activities.
Limited Visibility and Analysis: Manual processes often create data silos, hindering a comprehensive view of ESG performance and making it difficult to identify trends or areas for improvement.
Collaboration: Due to the fragmented nature of ESG data across departments, manual processes struggle to ensure consistent information sharing and collaboration.
Automating ESG data collection and reporting is a powerful solution to overcome the manual implementation challenges. It streamlines data collection and management by consolidating information from various sources into a central platform, ensuring accuracy and consistency.
Automated ESG assists in managing ESG KPIs, driving targets, initiating projects, and ensuring compliance. It also tracks ESG related risk contexts, allowing you to mitigate potential risks. And quickly get visual representation of data for reports. This enhanced transparency fosters better communication with stakeholders, allowing them to gain a clearer picture of a organization’s ESG commitment.
Benefits of Using ESG Software
- Increased Efficiency and Reduced Costs: By automating data collection, reporting, and analysis, organizations streamline processes and free up internal resources. This translates to significant cost savings and allows employees to focus on strategic initiatives that drive further ESG progress.
- Improved Data Quality and Consistency: The software consolidates information from disparate sources into a central platform, eliminating inconsistencies and errors that often plague manual data collection. This allows organizations to track progress and measure the effectiveness of their ESG initiatives with greater accuracy.
- Better Decision-Making and Risk Management: By identifying key trends, organizations can proactively address potential ESG risks and make informed decisions that align with their sustainability goals. This proactive approach mitigates potential regulatory issues and reputational damage, safeguarding the organization’s long-term success.
Criteria for ESG Software
- Comprehensiveness: Can the software collect and manage data across all relevant ESG categories?
- Data Automation: Does it offer functionalities to integrate with other applications or online forms, to minimize manual work and ensure data accuracy?
- Data Consolidation: Can it consolidate data from diverse sources into a central repository for easy access and analysis?
- Data Security: Does the software provide data security with robust encryption and access controls to safeguard sensitive ESG information?
- Customization: Does the software allow for customization of reports to meet specific stakeholder needs and regulatory requirements (GRI, SASB, etc.)?
- Data Visualization: Does it offer user-friendly data visualization tools (charts, graphs) to effectively communicate ESG performance and trends?
- Scalability: Can the software adapt and grow with the organization’s evolving ESG needs and data volume?
- Integration: Does it integrate seamlessly with existing enterprise systems (ERP, CRM) to streamline data flow and avoid siloed information?
- Ease of Use: Is the software user-friendly with an intuitive interface that empowers users across different departments to contribute and access ESG data?
Implementing a strong ESG strategy is no longer optional for businesses navigating the complexities of the modern world. Sustainability challenges demand a proactive approach, and ESG reporting enables organizations to assess their impact and operate responsibly. While manual implementation can be tedious, Automating ESG is a powerful tool to streamline data management, automate reporting, and empower data-driven decision making. By embracing the Automation of ESG, organizations can overcome implementation hurdles, build a more sustainable future, and achieve long-term success.
For more information, watch our video, join our webinar, or contact the experts.



